Blueprints
Ferro-gallate coated paper used for making copies before more conventional methods of printing were discovered.
Elevation - shows side or front of building.
Floor Plan -
A measured drawing to scale of the layout of a floor in a building.
- Interior walls and hallways
- Kitchen, laundry, restrooms
- Windows and doors
- Appliances such as stoves, refrigerators, water heater etc.
- Fireplaces, porch,
 1. Designed around the topography of the land, lot, and street.
1. Designed around the topography of the land, lot, and street.
Which side of your house is the sunny side?
2. Maximize convenience, minimize obstacles.
Unloading groceries - is the kitchen near the garage?
Dining room - is the table near the kitchen?
Laundry - is the laundry room near the bedrooms?
Closets - near front door? In master bathroom?
Bedrooms - are they secluded and private?
Stairs (two story houses give you more yard space) good location?
3. Open, or compartmentalized?
New homes are open - minimize hallways, maximize room sizes.
Loft ceilings, lots of windows, connected spaces.
4. Group bathrooms, kitchen, laudnry room, bar etc. to minimize plumbing walls.
R-Value:
Measure of thermal resistance of building. Under uniform conditions it is the ratio of the temperature difference across an insulator and the heat flux (heat transfer per unit area per unit time,
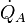 ) through it or
) through it or  .
. Bad (low R values: 1-4) create from too much glass, leaky windows/fireplace/doors, ventilation, thermal bridges etc.
- Too much glass

Red shows where most heat is lost - through the windows and roof.
Energy loss around windows can be fixed by using insulated double paned, coated, high quality ($$$) glass.
Some high-rise windows, are as low as a R-1 or R-1.4, offering not much more insulation than no window at all. ... Engineered windows can have R-values at R-8, R-11, or R-14.
link
Rule of thumb - anything more than 30% glass is going to waste energy.
Energy efficiency concerns: - Too leaky
Buildings don't have a requirement for air tightness, but energy conservation is dependent on air tightness. - Too much air - over ventilated
- Too many thermal bridges -

Steel studs - suck energy across a building (steel has high conductivity). Steel is 400 times more conductive than wood. (Have you ever seen a wood frying pan? Why not? Wood does not conduct heat.) How to insulate steel building? Insulate it around the outside - like pulling a sweater on (you don't eat the sweater, you put it on the outside of you)
U-factor or "U-value"
Overall heat transfer coefficient that describes how well a building element conducts heat.
U = k/L where k is the material's thermal conductivity and L is its thickness. Units of U arewatts per metres squared kelvin, or W/m²K.
A smaller U-factor is better at reducing heat transfer.A low U value usually indicates high levels of insulation.
The higher the U value, the worse the thermal performance of the building.
Buildings are made up of many different components (consider layers in walls/floors/roofs etc). U factors predict the composite behaviour of an entire building element rather than relying on the properties of individual materials.
** U-Factor" is used in the US to express the insulation value of windows, while R-value is used for insulation in the rest of the building( walls, floors, roofs). The rest of the world generally use U-Value/U-Factor for elements of the entire building envelope: including windows, doors, walls, roof & ground slabs.
Physics:
Heat flow: warm to cold
Moisture flow: warm to cold
Moisture flow: More to less
Air flow: High pressure to low pressure
If your AC is on:
inside cold, outside warm.
Heat and moisture flows from outside, to inside.
Vinal wallpaper - does not breathe - you'll get mold behind the wallpaper.
FEMA trailers in NEw Orleans - AC with No ventilation + vinal wallpaper in a hot humid climate

Rooftop exhaust system -
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rkfAcWpOYAA
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Alternative Housing
Cordwood Construction
http://www.cordwoodconstruction.org/http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cordwood_construction
Cob material:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cob_(material)
Small House movement:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Small_house_movement
Tiny House Layouts:
http://www.tinyhousedesign.com/road-limits-for-tiny-houses-on-trailers/
http://www.tumbleweedhouses.com/
Tree Houses
Doors:
Door swing - show the sweep of the door when opened and closed.

Need at least 2 exterior doors (2 exits for fire escape)
General rule - doors swing into a room.
Average size - used to be 32" by 6'8", now it's 3' by 6'8".
Simple Wall: two lines
Use Offset to create wall thicknesses.Interior walls are 2x4 (or 2 by 6 for load bearing), which is 3-1/2", plus 1/2" drywall on each side. Total = 4-1/2".
Outside wall, your framing will be either 2x4 or 2x6. This gives you 3-1/2" or 5-1/2", plus 1/2" for the drywall, 1/2" for the exterior sheathing (plywood), plus a 1" airspace between the wall and the brick, and 3-5/8" for the brick. Total = 9-1/8" or 11-1/8.
Windows: sash, glass, and sill (that bulges beyond the wall)

Line thickness:
Thicker lines are more important (walls)
Thin lines (counter tops, ceiling fans) are less important.
Use different layers for different object styles, ie, one layer for walls, one layer for windows, one for furniture, etc.

Living Room:



Couch sizes:

Dining Room:

Kitchen:
.jpg)

Bedroom:


Laundry:

Closet:

Bathroom:


Roof:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=81BlAB0SlA0
Roof Shapes:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_roof_shapes
Stairs:
Average for residential - 11" tread, 10"run. 8" riser,



No comments:
Post a Comment